Why a Balanced Diet Matters: Importance, Benefits, and a Practical Diet Chart

Table of Contents
ToggleSalient Features of a Balanced Diet
A balanced diet is key to maintaining overall health and well-being. Here are some essential features to keep in mind when planning your meals:
- Complex Carbohydrates Preferred: Opt for whole grains and fiber-rich sources of carbs for sustained energy.
- Carb Amount Based on Ideal Body Weight: Adjust your carbohydrate intake according to your body’s ideal weight for balanced nutrition.
- Avoid Processed and Ultra-Processed Foods: Minimize the consumption of foods high in additives and preservatives.
- Ensure Adequate Protein Intake: Incorporate enough protein from natural food sources like lean meats, legumes, and dairy.
- Moderation of Fat: Include fats in moderation, focusing on quality sources.
- Unsaturated Fats Over Saturated Fats: Prefer unsaturated fats like those from nuts, seeds, and olive oil for better heart health.
- 2-3 Servings of Seasonal Fruits: Ensure a variety of fresh, seasonal fruits in your diet for essential vitamins and minerals.
- Avoid Canned Juices: Fresh, homemade fruit juices are a healthier alternative to store-bought, sugar-laden canned juices.
- Healthy Snacking: Opt for nutrient-dense snacks like nuts, seeds, and fruits instead of unhealthy processed snacks.
- Avoid Bakery and Packed Foods: Minimize bakery items and pre-packaged foods, as they often contain unhealthy fats and excessive sugar.
Incorporating these features into your daily routine can help promote better health and a more balanced lifestyle.
The food nature gives us has incredible power to heal, energise, and support life, but in today’s world, fast food and other unhealthy options seem to have taken over. This has led to an increase in various lifestyle-induced health problems such as obesity, diabetes, and heart conditions. A balanced diet is not only a simple and effective solution to stay healthy, it also helps you recover faster from health problems. In this article, we’ll highlight the importance of a balanced diet, its benefits, and share a diet chart to guide you towards healthier eating habits. Let’s begin by understanding the definition of a balanced diet.
What is a balanced diet?
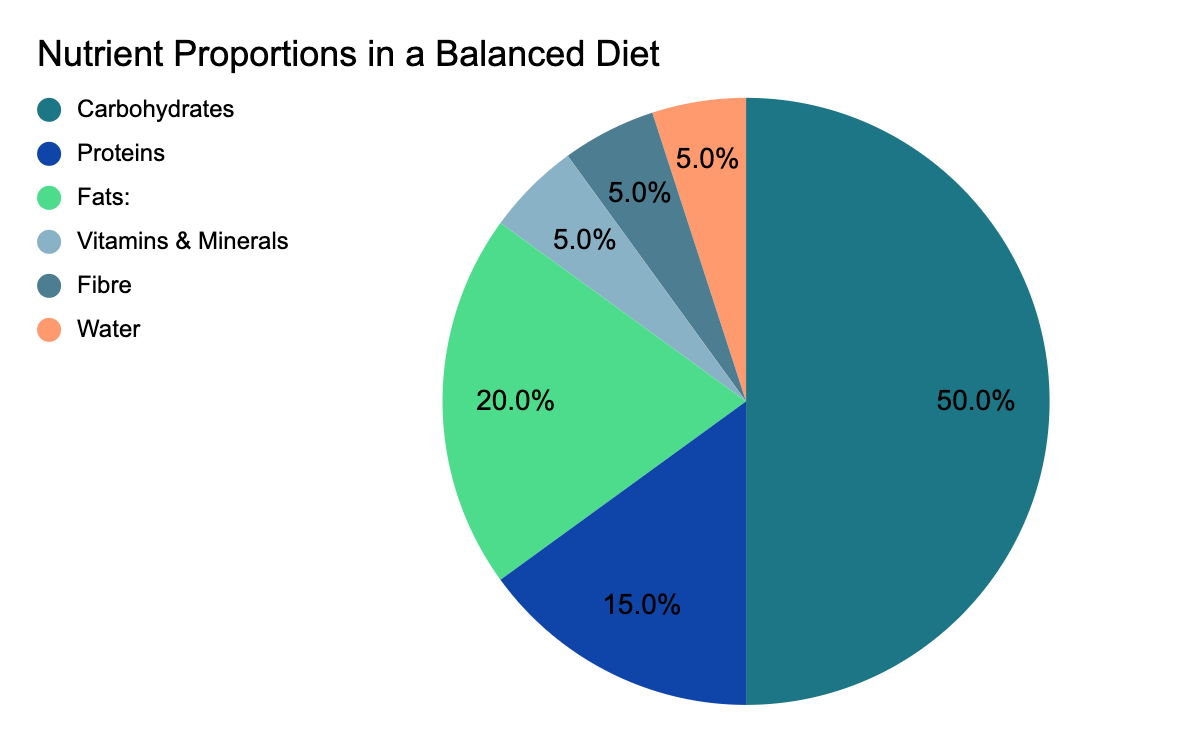
A balanced diet is a way of eating that provides your body with all the essential nutrients it needs to function optimally. It includes the right proportions of macronutrients (carbohydrates, proteins, and fats) and micronutrients (vitamins and minerals), along with fibre and water. Each component plays a vital role:
- Carbohydrates: Provide energy
- Proteins: Help build and repair tissues
- Fats: Support brain function and energy storage
- Vitamins and Minerals: Regulate bodily processes
Simply put, a balanced diet ensures that you consume a variety of foods in appropriate quantities to meet your body’s nutritional needs. Having said that, a balanced diet is not about strict limitations or cutting out entire food groups—it’s about creating a sustainable approach to eating foods that promote health and well-being.
Why is a Balanced Diet Important for Overall Health?
A balanced diet is vital for overall health because it ensures your body gets the nutrients it needs to function effectively. Here’s why it’s important:
- Energy and Vitality: A balanced diet provides the right mix of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, keeping you active and energised throughout the day.
- Immune Support: Essential vitamins and minerals, such as Vitamin C, Zinc, and Iron, strengthen your immune system, helping your body fight off illnesses and infections.
- Disease Prevention: Consuming a variety of nutrient-rich foods reduces the risk of chronic conditions such as hypertension, heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers.
- Weight Management: A balanced diet helps you keep your weight in check, by promoting metabolism, and aiding in weight loss or maintenance.
- Mental Well-being: Nutrients such as Omega-3 fatty acids and B vitamins contribute to improving focus, memory, and mood while reducing the risk of mental health issues such as anxiety and depression.
- Bone and Muscle Health: Calcium, Vitamin D, and proteins are crucial for strong bones and muscles, and help prevent conditions such as osteoporosis or age-related muscle loss.
- Digestive Health: Fibre-rich foods such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains improve digestion, prevent constipation, and promote a healthy gut microbiome.
- Long-term Vitality: By meeting your body’s nutritional needs, a balanced diet promotes longevity and a higher quality of life, keeping you healthy and active as you age.
Macronutrients: Building Blocks of a Balanced Diet
Macronutrients are the foundation of a balanced diet. They provide the energy and nutrients your body needs. There are three main macronutrients; proteins, carbohydrates, and fats, each playing a unique role in keeping your body healthy. Understanding these building blocks can help you make better food choices and maintain a nutritious diet. Let’s dive in.
Proteins
Proteins help build and maintain muscles, tissues, and organs, and they’re crucial for healing wounds and fighting off infections. Whether you’re lifting weights or recovering from a cold, proteins ensure your body stays strong and resilient. They’re also a key player in producing enzymes and hormones that keep everything running smoothly inside.
Sources of Protein: Animal and Plant
Proteins come from two primary sources: plants and animals. Let’s look at what they have to offer.
- Animal Based Protein: Animal-based proteins, found in eggs, chicken, fish, and dairy, are considered complete proteins as they contain all the essential amino acids the body needs to function properly. These proteins are especially beneficial for muscle repair and growth.
- Plant-based Proteins: Plant-based proteins, found in beans, lentils, tofu, nuts, and seeds, are not only rich in protein but also packed with fibre, vitamins, and minerals, which support heart health and digestion.
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are the body’s primary energy source. When you eat carbs, your body breaks them down into glucose, a type of sugar that serves as the main energy supply for your cells. This energy powers every activity, from basic functions like breathing and thinking to physical tasks like walking and exercising.
Without enough carbohydrates, the body struggles to maintain energy levels, leaving the person fatigued, irritable, and unfocused. Carbs are especially vital for brain function, as glucose is the brain’s preferred energy source. They also play a crucial role in muscle performance, especially during exercise or other physical activities. Simply put, carbohydrates are essential to keep your body and mind running at their best.
Types of Carbohydrates: Simple and Complex
Not all carbohydrates are created equal. Simple carbohydrates, found in sugary snacks, soft drinks, and processed foods, are quickly digested and provide a rapid energy boost. However, this energy is short-lived, often followed by a crash that leaves you feeling tired and hungry again. Overconsumption of simple carbs can lead to weight gain and blood sugar spikes, increasing the risk of health issues such as diabetes.
Complex carbohydrates are found in whole grains, beans, legumes, and vegetables. These carbs take longer to digest, providing a steady release of energy that keeps you fuelled throughout the day. They are also rich in fibre, which supports digestion and helps maintain stable blood sugar levels. Think of simple carbs as a quick fix and complex carbs as long-term fuel that sustains your body and promotes overall health.
Sources of Carbohydrates
Choosing the right carbohydrates can make a significant difference to your energy levels and overall health. Here are some of the healthiest sources of carbohydrates:
| Category | Examples |
| Whole Grains | Brown rice, quinoa, oats, barley |
| Fruits | Apples, bananas, berries, mangoes |
| Vegetables | Sweet potatoes, carrots, broccoli |
| Legumes | Lentils, chickpeas, kidney beans |
| Dairy & Alternatives | Milk, yogurt, soy milk, almond milk |
| Nuts & Seeds | Almonds, chia seeds, flaxseeds |
Fats
Fats are often misunderstood, but they are an essential part of a healthy diet. Far from being harmful, the right types of fats provide energy, support brain function, and help the body absorb vital fat-soluble vitamins like A, D, E, and K. Fats also protect your organs and contribute to healthy skin and hair. Including healthy fats in your diet supports overall well-being while also enhancing the flavour of your meals. Fats are categorised into three main types:
- Unsaturated Fats (Healthy Fats): Found in foods like avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil, and fatty fish, these fats help lower bad cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease.
- Saturated Fats: Found in butter, ghee, and red meat, these fats are fine in moderation but should be limited as excessive consumption can lead to heart-related issues.
- Trans Fats (Unhealthy Fats): Found in processed and fried foods, trans fats increase bad cholesterol and decrease good cholesterol, significantly raising the risk of heart disease. These should be avoided as much as possible.
Micronutrients: Small Yet Essential
Micronutrients are required in smaller quantities compared to macronutrients, but they are equally important. These nutrients, which include vitamins, minerals, fibre, and water, play a critical role in maintaining overall health. They regulate various bodily functions, support immunity, and ensure that your body operates efficiently. A lack of these nutrients may result in fatigue, weakened immunity, or long-term health problems.
Vitamins and Minerals
Vitamins and minerals are essential for various body functions:
- Vitamins: These organic compounds help your body convert food into energy, maintain healthy skin, support brain function, and protect cells from damage. Vitamin C, for instance, boosts immunity, while Vitamin D strengthens bones.
- Minerals: These are inorganic elements such as calcium, potassium, and iron that help build strong bones, maintain heart health, and carry oxygen in the blood. Calcium, for instance, supports bone health, while iron prevents anaemia.
A deficiency in these micronutrients can lead to severe health issues, such as scurvy (caused by lack of Vitamin C) or osteoporosis (caused by low calcium and Vitamin D). Consuming a variety of colourful fruits, vegetables, dairy products, and lean proteins ensures your body receives the required quantity of vitamins and minerals.
Fibre and Water
Fibre and water are often overlooked but are vital for maintaining a balanced diet:
- Fibre: Found in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, and legumes, and promotes digestive health by regulating bowel movements and preventing constipation. It also helps control blood sugar levels, lowers cholesterol, and keeps you feeling full for longer, aiding in weight management.
- Water: Water makes up about 60% of your body and is essential for survival, and helps regulate body temperature, transport nutrients, and flush out toxins. Staying hydrated improves digestion, supports joint health, and ensures that every cell in your body functions optimally.
By including plenty of water and fibre-rich foods in your diet, you can support digestion, stay energised, and maintain overall health.
Micronutrients may seem small, but they can greatly impact your health. Prioritising these nutrients in your diet is key to feeling your best and preventing long-term health issues.
Benefits of Eating a Balanced Diet
A balanced diet is the cornerstone of a healthy lifestyle. It provides the right mix of nutrients your body needs. Whether you’re an adult managing daily responsibilities or a growing child developing vital skills, a balanced diet can have profound benefits.
How Healthy Eating Benefits Adults
- Sustains Energy Levels: Provides steady energy throughout the day for productivity and focus.
- Reduces Risk of Chronic Diseases: Lowers the risk of heart disease, diabetes, obesity, and cancers.
- Supports Mental Health: Enhances brain function and reduces stress, anxiety, and depression.
- Strengthens Immunity: Boosts the immune system to fight infections and recover faster.
- Promotes Healthy Aging: Maintains bone density, muscle mass, and cognitive health, slowing ageing effects.
How Healthy Eating Benefits Children
- Promotes Growth and Development: Supports children’s physical and mental growth with essential nutrients.
- Boosts Brain Development: Enhances cognitive function, memory, and concentration for academic and social success.
- Strengthens the Immune System: Builds strong immunity to protect against frequent illnesses.
- Encourages Healthy Eating Habits: Instills lifelong healthy eating habits, reducing the risk of lifestyle diseases.
- Improves Behaviour and Mood: Stabilises mood swings and supports emotional well-being and energy balance.
Essential Components of a Balanced Diet
A balanced diet includes seven key nutrients that your body needs to function properly. Each nutrient has a specific role, and together they create a complete and nourishing diet. Here’s an overview:
| Nutrient | Function | Sources |
| Carbohydrates | Primary energy source for the body. | Whole grains, fruits, vegetables, legumes |
| Proteins | Builds and repairs tissues, supports muscle growth, and produces enzymes and hormones. | Meat, fish, eggs, beans, lentils, tofu |
| Fats | Provides long-term energy, supports brain function, and helps absorb fat-soluble vitamins. | Avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil, fish |
| Vitamins | Regulate bodily processes like metabolism and immunity. | Fruits, vegetables, dairy, whole grains |
| Minerals | Maintain healthy bones, teeth, and organ function. | Dairy, leafy greens, nuts, seafood |
| Fibre | Improves digestion and promotes gut health. | Whole grains, fruits, vegetables, legumes |
| Water | Essential for hydration, temperature regulation, and waste elimination. | Water, fruits, vegetables, soups |
A Sample Balanced Diet Plan for Healthy Eating
Here’s a simple and wholesome meal plan to help you incorporate a balanced diet into your daily routine, providing the essential nutrients your body needs.
- Breakfast: Oatmeal with almond milk, topped with fresh berries and chia seeds.
- Mid-Morning Snack: A handful of mixed nuts (almonds, walnuts).
- Lunch: Grilled chicken breast with quinoa and steamed broccoli.
- Afternoon Snack: An apple or a banana.
- Dinner: Baked salmon with sweet potato and a side salad (spinach, cucumber, olive oil dressing).
Debunking Myths About a Balanced Diet
There are many misconceptions about what a balanced diet really means, leading people to make unhealthy or unsustainable choices. Let’s address some common myths and uncover the truth:
Myth 1: A Balanced Diet Means Cutting Out All Fats
Truth: Not all fats are bad. Healthy fats, like those found in avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil, are essential for brain function, energy, and vitamin absorption. It’s trans fats and excessive saturated fats that should be limited.
Myth 2: Carbs Are the Enemy
Truth: Carbohydrates are your body’s primary energy source. The key is to choose complex carbs, like whole grains and vegetables, which provide sustained energy, rather than simple carbs found in sugary snacks.
Myth 3: A Balanced Diet Is Only for Weight Loss
Truth: A balanced diet isn’t just about managing weight—it’s about providing your body with the nutrients it needs to function well, prevent disease, and maintain energy and vitality, regardless of your weight goals.
Myth 4: You Have to Give Up Your Favourite Foods
Truth: A balanced diet is about moderation, not deprivation. You can enjoy your favourite treats occasionally as long as your overall diet is nutrient-rich and well-balanced.
Myth 5: All Plant-Based Diets Are Automatically Balanced
Truth: While plant-based diets can be healthy, they need careful planning to ensure all essential nutrients, like proteins, iron, and Vitamin B12, are included.
Myth 6: Supplements Can Replace Real Food
Truth: While supplements can help fill gaps in some cases, they cannot replicate the benefits of whole foods, which contain fibre, antioxidants, and a variety of nutrients that work together for optimal health.
Read More: Understanding Vitamin B12 Deficiency: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Practical Tips for Adopting a Balanced Diet
Making small, intentional changes to your eating habits can help you transition to a balanced diet with ease and sustainability.
- Add Variety: Include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, proteins, and healthy fats in every meal.
- Plan Ahead: Prepare a weekly meal plan and batch-cook to save time and stay on track.
- Control Portions: Use smaller plates and aim for balanced portions: half veggies, one-quarter protein, one-quarter grains.
- Snack Wisely: Choose healthy options like nuts, yogurt, or fruits instead of processed snacks.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water and limit sugary drinks and alcohol.
- Minimise Processed Foods: Opt for whole, fresh foods over packaged or fast foods.
- Read Labels: Check nutritional info to avoid added sugars, unhealthy fats, and excessive salt.
- Eat Mindfully: Focus on your meal, chew slowly, and avoid distractions while eating.
- Start Small: Make gradual changes like swapping white bread for whole grain or soda for water.
- Seek Guidance: Consult a nutritionist for personalised advice if needed.
Conclusion
Adopting a balanced diet is not just about improving your health; it’s about transforming your lifestyle to support long-term wellness and vitality. Small, consistent steps towards mindful eating can lead to big changes in your energy, mood, and overall well-being. Remember, the key is balance—enjoy a variety of foods, stay hydrated, and make sustainable choices that nourish your body and mind. At Graphic Era Hospital, we’re here to support you on your health journey. Whether you’re looking for personalised nutrition advice, wellness programs, or expert medical care, our dedicated team of dieticians is here to help. Take the first step today—book a consultation with our specialists and discover how we can help you achieve your health goals.
By Specialities
- Bariatric Surgery
- Cancer Care
- Cardiology
- Dental
- Dermatology
- Diabetes & Endocrinology
- Endocrinology and Diabetes
- ENT (Ear Nose Throat)
- Eye Care
- Gastroenterology
- Haematology
- Health Awareness
- Health Care
- Health Tips
- Hematology
- Hepatology
- Internal Medicine
- Mental Health and Behavioural Sciences
- Metabolic
- Neonatology
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Nutrition & Dietetics
- Obstetrics & Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Paediatric
- Physiotherapy & Rehabilitation
- Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
- Psychology
- Pulmonology
- Rheumatology
- Spine
- Urology
Recent Posts
- How Regular Heart Checkups Can Save Your Life
- World Kidney Day 2026: Prioritising Early Detection for Healthy Kidneys
- Invest in You: How to ‘Give to Gain’ Years of Wellness this International Women’s Day
- World Hearing Day 2026: Empower Yourself to Protect and Improve Your Hearing
- Understanding Dementia: Types, Causes, Symptoms and Treatment
Need expert medical advice?
Share your details and our healthcare specialists will reach out to assist you.
By proceeding, you acknowledge and agree to our Privacy Policy, Terms of Use, and Disclaimer.