Puffy Eyes Explained: Causes, Home Remedies, and Medical Treatments
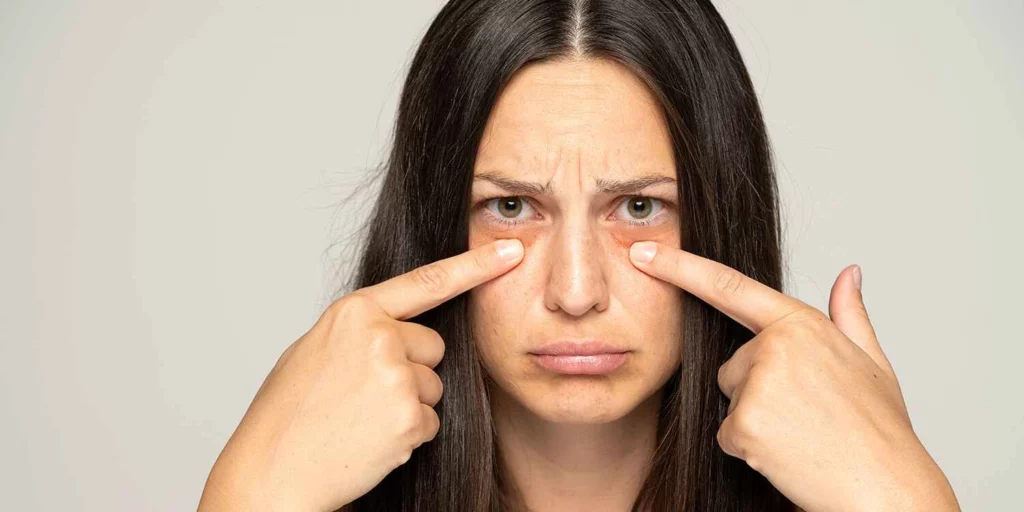

Waking up with puffy or swollen eyes is a common concern that can make you look tired and unwell. While occasional puffiness may be due to lack of sleep, dehydration, or excessive salt intake, persistent or severe swelling could signal an underlying issue such as allergies, fluid retention, or even a medical condition. When it comes to dealing with the problem; in many cases, simple home remedies can help. More severe or persistent puffiness may require medical treatment. This blog covers the common causes of puffy eyes and simple remedies you can try at home. If the puffiness lasts longer, we’ve also discussed medical treatments that may help. But first, let’s understand the problem.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Causes Puffy Eyes?
Puffy eyes can result from various factors, including lifestyle habits, allergies, aging, medical conditions, and environmental influences. Some causes are temporary, while others may require long-term management.
Lifestyle Factors
Lack of Sleep
Not getting enough rest can cause fluid to accumulate around the eyes, leading to puffiness and dark circles. Poor sleep also affects circulation, making the under-eye area appear dull and swollen. Over time, chronic sleep deprivation can weaken the skin’s elasticity, making puffiness more persistent.
High Salt Intake
Excessive salt in the diet leads to water retention, causing swelling in different parts of the body, including the delicate area around the eyes. Processed foods, salty snacks, and restaurant meals often contain high amounts of sodium, worsening puffiness. Staying hydrated and reducing salt intake can help minimise fluid buildup.
Excessive Alcohol Consumption
Alcohol dehydrates the body and disrupts the natural balance of fluids, which can make the skin appear puffy and tired. It also affects sleep quality, increasing the likelihood of waking up with swollen eyes. Limiting alcohol intake and drinking enough water can reduce its effects on the skin.
Smoking
Tobacco smoke contains harmful chemicals that break down collagen and elastin, leading to premature ageing and sagging skin. Reduced blood circulation also makes the skin under the eyes appear dull and swollen. Over time, smoking can contribute to chronic puffiness and fine lines.
Prolonged Screen Time
Staring at screens for long hours can cause eye strain, leading to fatigue and swelling around the eyes. Reduced blinking while using digital devices can result in dryness and irritation, making puffiness more noticeable. Taking breaks and using eye drops can help relieve strain and prevent swelling.
Allergies and Irritants
Seasonal Allergies
Pollen, dust, pet dander, and other allergens trigger an immune response that causes the body to release histamines. This leads to inflammation, swelling, redness, and itchiness around the eyes. Rubbing the eyes can worsen puffiness by further irritating the delicate skin.
Cosmetic Products
Certain skincare and makeup products may contain fragrances, preservatives, or harsh ingredients that irritate the skin around the eyes. Some people may experience mild swelling, redness, or itching after using specific products. Switching to hypoallergenic or fragrance-free products can help reduce irritation.
Contact Dermatitis
Some individuals develop allergic reactions to skincare ingredients, hair dyes, or even detergents, leading to puffiness and redness around the eyes. Identifying and avoiding the trigger can help prevent irritation and swelling.
Ageing and Genetics
Loss of Skin Elasticity
As the skin ages, it loses collagen and elasticity, making it more prone to sagging. The weakening of muscles around the eyes can also lead to fat shifting forward, creating a puffy appearance. While aging is unavoidable, certain skincare routines can help keep the skin firm for longer.
Genetic Predisposition
Some people are more prone to under-eye puffiness due to inherited traits. If puffy eyes run in the family, they may be present from a young age and persist despite lifestyle changes. In such cases, remedies may help reduce puffiness temporarily, but the condition is largely genetic.
Medical Conditions
Thyroid Disorders
Hormonal imbalances, particularly in hypothyroidism, can cause fluid retention, leading to persistent swelling around the eyes. In some cases, an overactive immune response related to thyroid conditions can also result in inflammation of the eye tissues.
Sinus Infections
Congestion from sinus infections can cause pressure to build up around the eyes, leading to puffiness. Blocked sinuses may also cause discomfort, headaches, and watery eyes. Treating the underlying sinus issue often helps in reducing puffiness.
Kidney or Liver Issues
When the kidneys or liver do not function properly, the body retains excess fluid, leading to swelling in various areas, including the face and eyes. If puffiness is persistent and accompanied by other symptoms, seeking medical advice is recommended.
Dermatological Conditions
Skin conditions such as eczema and dermatitis can cause inflammation, redness, and swelling around the eyes. The skin in this area is particularly sensitive, and flare-ups can make puffiness more prominent. Gentle skincare and prescribed treatments can help manage symptoms.
COVID-19
Eyelid swelling was reported in some COVID-19 patients during the pandemic, likely due to the body’s inflammatory response to the virus. This inflammation can cause swelling around the eyes, including the eyelids.
Environmental Factors
Weather Changes
Extreme weather conditions, such as high humidity or cold temperatures, can cause fluid retention and affect circulation, leading to puffiness. Seasonal shifts can also trigger allergies, making swelling around the eyes more noticeable.
Pollution
Exposure to pollutants, smoke, and other environmental toxins can irritate the skin and contribute to inflammation. Over time, pollution can weaken the skin’s barrier, making it more prone to dryness, puffiness, and premature aging. Cleansing the skin thoroughly and protecting it from pollutants can help maintain skin health.
Home Remedies for Puffy Eyes
Puffy eyes can often be managed with simple at-home remedies that help reduce swelling, improve circulation, and refresh the delicate under-eye area. These methods are effective for temporary puffiness caused by lifestyle factors, diet, or mild irritation.
Cold Compresses
Applying something cold to the eyes helps constrict blood vessels and reduce swelling. A chilled spoon, cold towel, or cucumber slices placed over closed eyelids for 10–15 minutes can provide quick relief. The cooling effect also soothes tired eyes and reduces redness.
Hydration and Diet
Drinking enough water helps prevent fluid retention, a common cause of puffiness. Reducing salt intake, especially from processed foods, can also help balance fluids in the body. Including anti-inflammatory foods like berries, leafy greens, and nuts in the diet may further support skin health and reduce swelling.
Sleep Hygiene
Getting enough quality sleep allows the body to repair and regulate fluid balance. Sleeping with the head slightly elevated can prevent fluid from pooling around the eyes overnight, reducing puffiness in the morning. Aim for at least 7–9 hours of rest to keep the skin looking refreshed.
Natural Topical Treatments
Certain natural ingredients can help soothe and tighten the under-eye area:
- Tea Bags – Caffeinated tea bags contain tannins and antioxidants that reduce swelling and improve circulation. Herbal tea bags, like chamomile, have anti-inflammatory effects that can calm irritation.
- Aloe Vera Gel – Known for its cooling and soothing properties, aloe vera can help reduce puffiness and hydrate the skin. Apply a small amount under the eyes and leave it on for a few minutes before rinsing.
- Potato Slices or Juice – Potatoes have natural astringent properties that may help tighten the skin and reduce swelling. Thin slices or potato juice applied to the under-eye area for 10–15 minutes can provide relief.
Facial Massage and Exercises
Gentle massage techniques can improve lymphatic drainage and reduce fluid buildup around the eyes. Light tapping with fingertips or using a jade roller in an outward motion helps promote circulation. Regular facial exercises may also strengthen the muscles around the eyes, preventing sagging and puffiness over time.
Medical Treatments for Puffy Eyes
If puffy eyes persist despite home remedies, medical treatments may be necessary. The right approach depends on the underlying cause, whether it’s allergies, fluid retention, or skin laxity due to aging.
Prescription Medications
For puffiness caused by allergies or inflammation, a doctor may recommend:
- Antihistamines – Help reduce swelling caused by allergic reactions to pollen, dust, or pet dander.
- Corticosteroid Creams – Used in cases of skin conditions like eczema or dermatitis that contribute to under-eye puffiness.
- Diuretics – May be prescribed in cases of fluid retention linked to kidney or heart issues, though they are not typically used for mild puffiness.
Dermatological Procedures
Certain non-invasive treatments can help tighten the skin and reduce puffiness:
- Laser Therapy – Stimulates collagen production, improving skin elasticity and reducing under-eye swelling.
- Chemical Peels – Removes damaged skin layers, helping to improve skin texture and reduce puffiness caused by aging.
- Microneedling – Boosts collagen and improves circulation in the under-eye area, reducing mild puffiness over time.
Injectable Treatments
For more persistent puffiness caused by fat deposits or loss of skin elasticity, doctors may suggest:
- Dermal Fillers – Hyaluronic acid fillers can smooth out under-eye hollows and reduce the appearance of puffiness by balancing volume loss.
- Botox – Botox can help relax muscles around the eyes, improving overall appearance and preventing fine lines that can make swelling more noticeable.
Surgical Options
In cases of chronic puffiness due to fat deposits or sagging skin, surgical procedures may be considered:
- Blepharoplasty (Eyelid Surgery) – Removes or repositions excess fat and tightens the skin around the eyes, offering a long-term solution for persistent puffiness.
- Fat Transfer or Removal – In some cases, redistributing or removing fat can help correct under-eye bags that contribute to puffiness.
Read more- Why a Balanced Diet Matters: Importance, Benefits, and a Practical Diet Chart
Prevention Tips
Preventative measures focus on minimising fluid retention, protecting the delicate under-eye area, and maintaining overall skin health.
- Maintain a healthy sleep routine: Getting 7–9 hours of quality sleep each night allows the body to regulate fluid balance and repair the skin. Sleeping with the head slightly elevated prevents fluid from accumulating around the eyes, reducing morning puffiness.
- Stay hydrated and eat a balanced diet: Drinking enough water throughout the day prevents dehydration-related fluid retention. Limiting salt intake, especially from processed and fast foods, can also help minimise swelling. Including anti-inflammatory foods like leafy greens, berries, and nuts in the diet supports skin health and reduces under-eye puffiness.
- Reduce eye strain and screen time: Prolonged screen use can cause eye fatigue and puffiness. Taking regular breaks, adjusting screen brightness, and using blue light filters can reduce strain. Applying the 20-20-20 rule (looking away from the screen every 20 minutes at something 20 feet away for 20 seconds) helps relax the eye muscles.
- Protect the skin from allergens and irritants: For those prone to allergies, minimising exposure to dust, pollen, pet dander, and strong fragrances can help prevent swelling. Using hypoallergenic skincare and cosmetics, along with regularly washing pillowcases, reduces irritation around the eyes.
- Avoid smoking and limit alcohol: Smoking accelerates collagen breakdown, leading to premature skin sagging and puffiness. Excessive alcohol consumption causes dehydration and fluid retention, worsening under-eye swelling. Reducing or avoiding both can help maintain healthy, firm skin.
- Practice gentle skincare: Using a mild cleanser and hydrating eye cream keeps the skin around the eyes nourished and less prone to irritation. Removing makeup before bed prevents clogged pores and irritation that can lead to puffiness. When applying products, using a light tapping motion instead of rubbing helps prevent skin damage.
- Manage stress levels: Chronic stress can contribute to poor sleep, inflammation, and fluid retention. Practicing stress management techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or regular physical activity can support overall well-being and prevent puffiness.
When to Consult a Doctor?
Puffy eyes are usually harmless and can be managed with home remedies or lifestyle changes. However, in some cases, they may indicate an underlying health condition that requires medical attention. It is advisable to consult a doctor if:
- Persistent or worsening puffiness – Swelling that does not improve despite home remedies and lifestyle changes, lasting for several weeks.
- Severe swelling or pain – Sudden, intense puffiness, especially if accompanied by tenderness, warmth, or discomfort, which could indicate an infection or allergic reaction.
- Changes in vision – Blurry vision, double vision, or difficulty focusing, which may signal a serious condition like orbital cellulitis.
- Redness, itching, or discharge – Symptoms such as excessive redness, irritation, or eye discharge, which could suggest conjunctivitis, blepharitis, or an allergic reaction.
- Swelling in other areas – Puffiness that occurs along with swelling in the legs, hands, or face, which may indicate fluid retention due to kidney, liver, or heart conditions.
- Dark circles or skin changes – Unusual darkening, thinning, dryness, or persistent irritation of the skin around the eyes, possibly pointing to an underlying dermatological issue.
Final Words
If puffy eyes have become a frequent concern, it may be time to look beyond home remedies. At Graphic Era Hospital, our dermatologists and ophthalmologists can assess the cause of persistent puffiness and recommend the right treatment for you. If your symptoms have been ongoing or accompanied by discomfort, schedule a consultation to ensure your eye health is in good hands.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can dehydration cause puffy eyes?
Yes, dehydration can lead to puffy eyes. When the body lacks sufficient water, it tries to retain fluids, which can result in swelling around the eyes. Staying hydrated helps maintain fluid balance and reduces the likelihood of puffiness.
Do certain medications contribute to under-eye puffiness?
Some medications can cause fluid retention, leading to puffiness around the eyes. Common culprits include corticosteroids, antihypertensives, hormonal treatments, and certain antidepressants. If you suspect a medication is affecting your eyes, consult your doctor before making any changes to your prescription.
Is it normal for one eye to be puffier than the other?
Mild asymmetry in puffiness is common and can be due to sleeping position, fluid retention, or minor irritation. However, if one eye becomes significantly swollen, painful, or accompanied by vision changes, it may indicate an infection, injury, or another medical issue that requires attention.
Can frequent eye rubbing make puffiness worse?
Yes, rubbing your eyes frequently can worsen puffiness by irritating the delicate skin around them. This can lead to inflammation, increased fluid retention, and even broken blood vessels, making the area appear swollen or discoloured. If irritation is persistent, addressing the underlying cause, such as allergies or dryness, can help.
How does hormonal imbalance affect eye puffiness?
Hormonal fluctuations, particularly during menstruation, pregnancy, or menopause, can cause fluid retention, leading to puffiness around the eyes. Thyroid imbalances, especially hypothyroidism, can also contribute to persistent swelling. If puffiness occurs alongside other symptoms like fatigue or weight changes, medical evaluation may be necessary.
Are there any supplements that help reduce puffy eyes?
Certain supplements may help reduce puffiness by supporting skin health and fluid balance. Omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin C, and flavonoid-rich supplements like quercetin can help reduce inflammation. Potassium can aid in balancing sodium levels, which may prevent fluid retention. However, it’s best to consult a doctor before starting any new supplements.
How long does it usually take for puffy eyes to go away?
The duration of puffy eyes depends on the cause. Temporary swelling from sleep deprivation, diet, or minor irritation typically subsides within a few hours. Allergic reactions or fluid retention may take longer, often improving within a day. If puffiness persists for weeks without improvement, it may be worth seeking medical advice.
By Specialities
- Bariatric Surgery
- Cancer Care
- Cardiology
- Dental
- Dermatology
- Diabetes & Endocrinology
- Endocrinology and Diabetes
- ENT (Ear Nose Throat)
- Eye Care
- Gastroenterology
- Haematology
- Health Awareness
- Health Care
- Health Tips
- Hematology
- Hepatology
- Internal Medicine
- Mental Health and Behavioural Sciences
- Metabolic
- Neonatology
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Nutrition & Dietetics
- Obstetrics & Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Paediatric
- Physiotherapy & Rehabilitation
- Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
- Psychology
- Pulmonology
- Rheumatology
- Spine
- Urology
Recent Posts
Need expert medical advice?
Share your details and our healthcare specialists will reach out to assist you.
By proceeding, you acknowledge and agree to our Privacy Policy, Terms of Use, and Disclaimer.