What is Sunburn? Causes, Symptoms, and Skin Care Tips
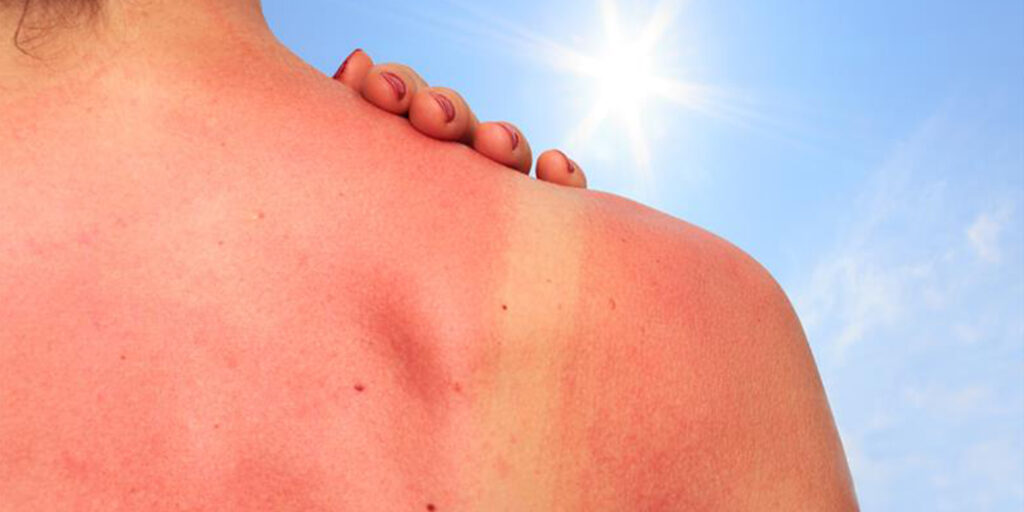

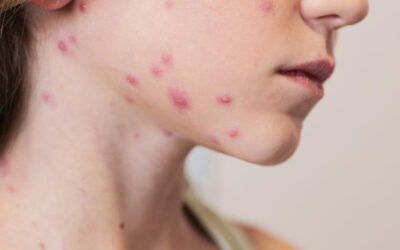
Sunburn is more than just a temporary redness after a day in the sun; it’s an evident sign of skin damage caused by ultraviolet (UV) rays. In India, where high temperatures and prolonged sunlight are common for most of the year, sunburn remains a common concern. Whether it occurs during outdoor travel, daily commutes, or seasonal heatwaves, sunburn can affect anyone regardless of skin tone. While most cases are mild and resolve on their own, repeated or severe episodes can lead to complications that affect long-term skin health.
In this article, we’ll explore what sunburn is, how it develops, the signs to watch for, effective ways to manage the discomfort, and practical skin protection tips that are suitable for Indian conditions. Let’s start by understanding the basics.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is Sunburn?
Sunburn refers to the skin’s inflammatory response to excessive exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, primarily from the sun. When the skin absorbs more UV rays than it can safely handle, it triggers damage to the outermost layer, leading to redness, warmth, pain, and in some cases, peeling or blistering.
Two main types of UV rays are responsible for sunburn: UVB rays, which directly damage the surface layers of the skin, and UVA rays, which penetrate deeper and contribute to long-term effects such as ageing and pigmentation. Both types can harm the skin without immediate warning signs, especially in tropical climates where sun intensity is higher.
The body responds to this damage by increasing blood flow to the affected area, which is why the skin turns red and feels hot. In some cases, the immune system may also react by causing swelling or fluid accumulation, resulting in blisters.
Common Causes and Risk Factors
Sunburn can develop even after a short period of sun exposure, particularly when proper skin protection is not used. Several factors can increase the risk of getting sunburned, especially in a country like India where the sun is intense for most of the year. Common causes include:
- Spending extended time outdoors during peak sunlight hours, typically between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m.
- Skipping sunscreen or using one with inadequate sun protection factor (SPF).
- Engaging in outdoor activities such as travel, sports, or gardening without protective clothing or shade.
- Exposure to reflective surfaces such as water, sand, or snow, which intensify UV rays.
Risk factors that increase vulnerability:
- Having fair or sensitive skin that burns easily
- Infants, young children, and elderly individuals with more delicate skin
- People with medical conditions or undergoing treatments that increase sun sensitivity (such as retinoids or certain antibiotics)
- Residing in high-altitude or tropical areas where the sun’s rays are stronger
Recognising these triggers and vulnerabilities is key to avoiding repeated or severe sunburn.
Symptoms of Sunburn
Sunburn symptoms usually appear a few hours after sun exposure, though in some cases they may take longer to fully develop. The severity can vary depending on the duration and intensity of UV exposure, as well as the individual’s skin type. Common signs and symptoms include:
- Redness and warmth over the affected skin
- Pain or tenderness, especially when the area is touched
- Swelling or tightness in the skin
- Itching or irritation as the skin begins to heal
- Blisters, which may form in cases of moderate to severe sunburn
- Peeling, typically occurring a few days after the burn as damaged skin sheds
- Fever, chills, fatigue, or nausea in cases of extensive sunburn or when large areas of skin are affected
While mild sunburn often resolves within a few days, severe cases may require medical attention, especially when accompanied by dehydration, dizziness, or intense discomfort.
Read More: https://geimshospital.com/blog/dry-skin-in-winter/
Why the Face Is More Vulnerable to Sunburn
The face is one of the most commonly sunburned areas of the body. This is largely due to its constant exposure to sunlight, even during routine activities such as walking, driving, or sitting near windows. Unlike other parts of the body, the face is rarely covered and often left unprotected.
Facial skin is also thinner and more sensitive, making it more prone to damage from ultraviolet rays. Areas such as the forehead, nose, cheeks, and lips are especially vulnerable. Sunburn on the face not only causes immediate discomfort but can also lead to long-term issues, including pigmentation, uneven skin tone, and premature ageing. In individuals with acne or other skin conditions, sunburn can worsen irritation and slow down the healing process.
Protecting the face with appropriate skincare, sunscreen, and physical barriers such as hats or scarves is essential, particularly in Indian climates where the sun can be harsh even during shorter exposures.
Complications of Severe or Repeated Sunburn
While mild sunburn may heal on its own, repeated or intense episodes can lead to deeper skin damage and longer-term health concerns. The skin, being the body’s first line of defence, becomes compromised when exposed to harmful UV radiation too often or too severely. Common complications include:
- Peeling and prolonged skin sensitivity that may take several days to settle
- Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, especially common in Indian skin tones, leading to uneven skin patches or dark spots
- Sunspots or actinic keratosis, which are rough, scaly patches caused by long-term sun damage
- Premature ageing, including wrinkles, fine lines, and a leathery skin texture due to collagen breakdown
- Increased risk of skin cancer, such as basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and in rare cases, melanoma
- Eye damage, especially when the sunburn affects the area around the eyes or if proper eyewear isn’t used
Home Remedies and First Aid for Sunburn
Mild to moderate sunburn can often be managed at home with simple measures that help soothe the skin and promote healing. The goal is to cool the affected area, reduce inflammation, and keep the skin well-hydrated. Effective home care tips include:
- Cool compresses: Gently applying a cold, damp cloth to the skin can reduce heat and discomfort.
- Fragrance-free moisturisers: Applying a gentle, non-perfumed moisturiser prevents dryness and supports skin repair.
- Staying hydrated: Drinking plenty of fluids helps restore moisture levels and prevents dehydration.
- Avoiding further sun exposure: Staying indoors or in the shade is important until the skin has fully healed.
It’s advisable to avoid harsh soaps, scrubs, or exfoliants until the skin recovers. Letting the skin heal naturally without picking at blisters or peeling areas can also prevent scarring or secondary infections.
When to See a Doctor
While most cases of sunburn can be treated at home, certain signs may indicate a more serious condition that requires medical attention. Delaying care in such situations can increase the risk of complications, especially for vulnerable individuals such as children, the elderly, or those with pre-existing skin conditions.
It is advisable to consult a doctor if:
- The sunburn is severe or widespread, covering a large area of the body
- Blisters are extensive or become painful, swollen, or filled with pus
- There are signs of infection, such as increased redness, warmth, or discharge from the affected area
- The individual experiences fever, chills, nausea, or dizziness
- The skin does not start to heal within a few days or becomes progressively worse
- Infants or elderly individuals are affected, as they are more prone to dehydration and complications
Early medical intervention can help manage discomfort, prevent further damage, and support faster recovery, particularly in cases where sunburn leads to fluid loss or serious inflammation.
How to Prevent Sunburn: Tips for Indian Skin
Preventing sunburn involves a combination of sun protection habits and skincare choices that suit the Indian climate and skin types. Since UV radiation can cause damage even on cloudy days, consistent protection is essential throughout the year and not just in summer.
Practical sun protection tips
- Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher. Look for formulas that suit Indian skin, such as those that are lightweight, non-greasy, and sweat-resistant.
- Apply sunscreen generously on all exposed areas, including the face, neck, ears, and arms. Reapply every two to three hours, especially after sweating or washing the face.
- Wear protective clothing, such as long-sleeved cotton outfits, wide-brimmed hats, and UV-protective sunglasses when outdoors.
- Seek shade whenever possible, especially between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m., when the sun’s rays are the strongest.
- Avoid direct sun exposure for babies and toddlers, as their skin is highly sensitive to UV damage.
Additional tips for Indian skin care
- Choose hydrating foods and drinks such as coconut water, buttermilk, watermelon, and cucumbers to support skin health from within.
- Incorporate natural soothers like rose water or sandalwood paste to cool the skin after sun exposure.
- Opt for lightweight, breathable fabrics that allow airflow and reduce heat retention.
Final Thoughts
Sunburn is often underestimated, especially when the symptoms appear mild at first. However, even a single episode can cause lasting effects on the skin if not managed properly. In a country like India, where sun exposure is frequent and often intense, understanding the signs of sunburn and knowing how to prevent it is essential for maintaining healthy skin. Early care, protective habits, and attention to skin changes can make a significant difference in long-term skin health.
For expert advice on skin protection and treatment, consult the dermatology team at Graphic Era Hospital. Timely care can prevent complications and ensure your skin stays healthy and well-protected through every season.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can sunburn happen even on cloudy days?
Yes, up to 80% of UV rays can pass through clouds. This means sunburn is still possible even when the sky is overcast, especially during prolonged outdoor exposure.
Is peeling skin after sunburn normal?
Yes, peeling is a natural part of the healing process. It occurs when the body sheds damaged skin cells. It’s important not to pick or peel the skin to avoid scarring or infection.
How often should sunscreen be reapplied?
Sunscreen should be reapplied every two to three hours, or more frequently if sweating, swimming, or washing the face.
Does melanin protect against sunburn completely?
Melanin offers some natural protection, which is why darker skin may take longer to burn. However, it does not make the skin immune to UV damage or the risk of long-term complications.
Can sunburn affect the eyes too?
Yes, excessive UV exposure can irritate the eyes and cause photokeratitis, often referred to as “sunburn of the eyes.” Wearing UV-protective sunglasses is important for eye safety.
By Specialities
- Bariatric Surgery
- Cancer Care
- Cardiology
- Dental
- Dermatology
- Diabetes & Endocrinology
- Endocrinology and Diabetes
- ENT (Ear Nose Throat)
- Eye Care
- Gastroenterology
- Haematology
- Health Awareness
- Health Care
- Health Tips
- Hematology
- Hepatology
- Internal Medicine
- Mental Health and Behavioural Sciences
- Metabolic
- Neonatology
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Nutrition & Dietetics
- Obstetrics & Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Paediatric
- Physiotherapy & Rehabilitation
- Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
- Psychology
- Pulmonology
- Rheumatology
- Spine
- Urology
Recent Posts
Need expert medical advice?
Share your details and our healthcare specialists will reach out to assist you.
By proceeding, you acknowledge and agree to our Privacy Policy, Terms of Use, and Disclaimer.